The U.S. Food and Drug Administration today approved Mavyret (telaprevir and pibrentasvir) tablets to treat all six genotypes of hepatitis C virus (HCV) in children ages 12 to 17. Mavyret was previously approved to treat HCV in adults in 2017.
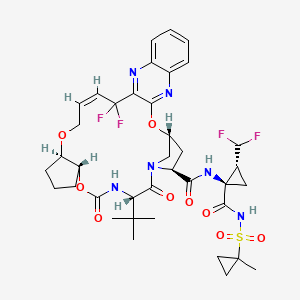
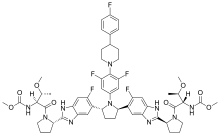 Pibrentasvir
Pibrentasvir
Glecaprevir
“Direct-acting antiviral drugs reduce the amount of HCV in the body by preventing the virus from multiplying, and in most cases, they cure HCV infection,” said Jeffrey Murray, M.D., M.P.H., deputy director of the Division of Antiviral Products in the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research. “Today’s approval represents another treatment option for children and adolescents with HCV infection, but for the first time, in all genotypes of HCV.”
HCV is a viral disease that causes inflammation of the liver that can lead to diminished liver function or liver failure. According to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, an estimated 2.7 to 3.9 million people in the U.S. have chronic HCV, and children born to HCV-positive mothers are at risk for HCV infection. It is estimated that there are 23,000 to 46,000 children in the U.S. with HCV infection.
With today’s approval, dosing information is provided for Mavyret for the treatment of adult or pediatric patients 12 years and older, or weighing at least 99 pounds, who are infected with any of six identified HCV genotypes either without cirrhosis or with compensated cirrhosis.
The safety and efficacy of Mavyret in pediatric patients was evaluated during clinical trials of 47 patients with genotype 1, 2, 3 or 4 HCV infection without cirrhosis or with mild cirrhosis. Results of the trials demonstrated that 100 percent of patients who received Mavyret for eight or 16 weeks had no virus detected in the blood 12 weeks after finishing treatment, suggesting that patients’ infection had been cured. In pediatric patients with cirrhosis, history of a kidney and/or liver transplant, or genotype 5 or 6 HCV infection, the safety and efficacy of Mavyret are supported by previous studies observed in glecaprevir and pibrentasvir in adults. The adverse reactions observed were consistent with those observed in clinical studies of Mavyret in adults.
Treatment duration with Mavyret differs depending on treatment history, viral genotype and cirrhosis status. The most common adverse reactions in patients taking Mavyret were headache and fatigue. Mavyret is not recommended in patients with moderate cirrhosis and contraindicated in patients with severe cirrhosis. It is also contraindicated in patients taking the drugs atazanavir and rifampin.
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) reactivation has been reported in HCV/HBV coinfected adult patients who were undergoing or had completed treatment with HCV direct-acting antivirals, and who were not receiving HBV antiviral therapy. HBV reactivation in patients treated with direct-acting antiviral medicines can result in serious liver problems or death in some patients. Health care professionals should screen all patients for evidence of current or prior HBV infection before starting treatment with Mavyret.
https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB13879
https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Glecaprevir#section=Structures
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pibrentasvir
https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Pibrentasvir











