
Allergan plc, a leading global pharmaceutical company, announced the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved the company's supplemental New Drug Application (sNDA) for Teflaro (ceftaroline fosamil), granting new indications for pediatric patients 2 months of age to less than 18 years of age with acute bacterial skin and skin structure infections (ABSSSI), including infections caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), and community-acquired bacterial pneumonia (CABP) caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae and other designated susceptible bacteria.
"The impact of ABSSSI and CABP among children is significant, as these infections often require hospitalization and are met with limited pediatric treatment options, particularly as resistance increases among the pathogens that cause these infections," said David Nicholson, Chief R&D Officer, Allergan. "These new indications are yet another testament to our ongoing research and development in anti-infectives to address the evolving challenges of serious infections. Importantly, it allows us to educate physicians on the data they need to prescribe Teflaro to appropriate pediatric patients in need of an option that is safe and effective against some of the most difficult-to-treat pathogens in ABSSSI and CABP."
ABSSSI and CABP are common causes of healthcare visits and hospitalizations among children. Studies show more than 70,000 hospitalizations for ABSSSI occur among children per year – a rate that has more than doubled over the past 13 years.1 A study conducted by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) also found children younger than 5 years of age accounted for 70 percent of children hospitalized for community-acquired pneumonia.
These new indications were approved based on results from clinical studies evaluating TEFLARO in pediatric patients (2 months to less than 18 years of age), including one active-controlled study in ABSSSI and two active-controlled studies in CABP. In the ABSSSI active-controlled study, the efficacy and safety of Teflaro was compared with vancomycin or cefazolin (each with optional aztreonam). In the CABP studies, Teflaro was compared with ceftriaxone. Use of Teflaro in pediatric patients 2 months to less than 18 years of age is supported by evidence from adequate and well-controlled studies of Teflaro in adults, as well as additional pharmacokinetic and safety data from pediatric trials.
The primary objective of the pediatric ABSSSI and CABP studies was to evaluate the safety and tolerability of Teflaro. These studies were not powered for comparative inferential efficacy analysis, and no efficacy endpoints were identified as primary.
To evaluate the treatment effect of Teflaro in the ABSSSI pediatric trial, an analysis was conducted in 159 patients with ABSSSI in the Modified Intent-to-Treat (MITT) population. This analysis evaluated responder rates based on achieving both cessation of lesion spread and absence of fever on Study Day 3. Patients treated with Teflaro showed a higher response at Study Day 3 versus the comparator group, with clinical response achieved in 80.4 percent (86/107) of patients treated with Teflaro and 75 percent (39/52) of patients in the comparator group, with a treatment difference of 5.4 percent (95 percent Confidence Interval [CI] -7.8, 20.3). Clinical cure rates at the test of cure (TOC) visit (8 to 15 days after the end of therapy) for the ABSSSI pediatric trial were 94.4 percent (101/107) for patients treated with Teflaro and 86.5 percent (45/52) for the comparator, with a treatment difference of 7.9 (95 percent CI -1.2, 20.2).
To evaluate the treatment effect of Teflaro in the CABP trial submitted for this pediatric filing, an analysis was conducted in 143 patients with CABP in the MITT population. This analysis evaluated responder rates at Study Day 4 based on achieving improvement in at least two out of seven symptoms (cough, dyspnea, chest pain, sputum production, chills, feeling of warmth/feverish and exercise intolerance or lethargy), and worsening in none of these symptoms. The clinical response at Study Day 4 was 69.2 percent (74/107) for patients treated with Teflaro and 66.7 percent (24/36) for the comparator, with a treatment difference of 2.5 percent (95 percent CI -13.9, 20.9). Clinical cure rates at TOC were 87.9 percent (94/107) for patients treated with TEFLARO and 88.9 percent (32/36) for the comparator, with a treatment difference of -1.0 (95 percent CI -11.5, 14.1).
Results from the clinical studies in pediatric patients showed that Teflaro demonstrated a safety profile that was compatible with treatment of ABSSSI and CABP at the clinical dosages studied. The safety findings were similar to those seen in the adult studies, and no safety concerns were identified beyond those already known to be cephalosporin class effects.
Teflaro is the first and only cephalosporin indicated in adults and pediatric patients 2 months of age and older for the treatment of ABSSSI and CABP due to designated susceptible pathogens that can be administered by intravenous (IV) infusion in five minutes to one hour.

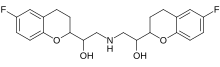
 Valsartan
Valsartan




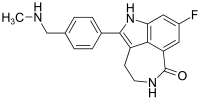

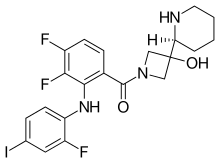 Cobimetinib
Cobimetinib 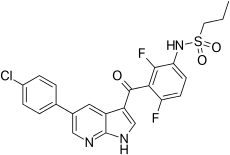 vemurafenib
vemurafenib 