In continuation of my update on dapagliflozin, and metformin hydrochloride

Dapagliflozin 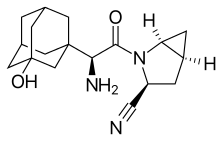 Saxagliptin and
Saxagliptin and  (Metformin)
(Metformin)
 Saxagliptin and
Saxagliptin and
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved Qternmet XR(dapagliflozin, saxagliptin and metformin hydrochloride) extended release tablets as an oral adjunct treatment to diet and exercise to improve glycaemic control in adults with type-2 diabetes (T2D).
The approval is based on two Phase III trials, which evaluated combinations of dapagliflozin and saxagliptin on a background of metformin over 24 weeks, in patients with inadequately-controlled T2D.
In one trial, treatment with 5mg dapagliflozin/5mg saxagliptin in addition to metformin demonstrated statistically-significant decreases in HbA1c (average blood glucose levels), and an increase in the number of patients achieving the recommended HbA1c treatment goal of <7%. In the second trial, treatment with 10mg dapagliflozin/5mg saxagliptin in addition to metformin extended release demonstrated statistically-significant decreases in HbA1c, and an increase in the number of patients achieving an HbA1c <7%.
The safety results of the individual medicines in these trials were consistent with their known profile.
About Qternmet XR
Qternmet XR is a once-daily, oral medicine compromised of the selective sodium‑glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT-2) inhibitor dapagliflozin, the dipeptidyl peptidase‑4 (DPP‑4) inhibitor saxagliptin and metformin hydrochloride extended release. Qternmet XR is approved in the US as an adjunct to diet and exercise to improve glycaemic control in adults with type-2 diabetes.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dapagliflozin
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Saxagliptin
https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB06335
https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00331
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Metformin




