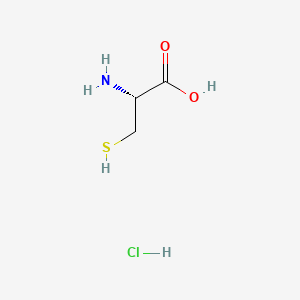
Avadel Pharmaceuticals plc (Nasdaq: AVDL) announced today that the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved Nouress (AV001), a cysteine hydrochloride injection, a critical drug for treating neonatal patients requiring total parenteral nutrition (TPN).
In addition, Avadel announced today that the United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) recently issued United States Patent No. 10,493,051 covering cysteine solutions, including the approved Nouress product. This patent is listed in the Orange Book for Nouress and is set to expire in March of 2039. Avadel has additional U.S. patent applications pending for Nouress.
“We are pleased to receive FDA approval for Nouress, which validates our strategy of developing innovative medicines for patients,” said Greg Divis, Chief Executive Officer of Avadel. “Nouress is the fourth FDA approved product in our sterile injectable hospital business. The cash flow generated by this legacy business is supporting the clinical development costs from our lead program, FT218, which is currently expected to announce topline data from the pivotal Phase 3 REST-ON trial in the second quarter of 2020. We believe that as a once-nightly formulated sodium oxybate, FT218, if approved by the FDA, has the potential to take a significant share of the twice-nightly sodium oxybate market, which is currently valued at an estimated annualized rate of $1.7 billion.”
Avadel is currently evaluating the timing and process for a commercial launch of Nouress in the United States. In this regard, a competitor received FDA approval earlier this year for its cysteine hydrochloride injection and more recently was granted a U.S. patent, which Avadel is assessing along with other market factors.
Due to a historical lack of reliable supply, U.S. markets previously imported cysteine hydrochloride injection from Canada under special FDA rules allowing shortage drugs to be sourced abroad if no domestic supplies are available. With FDA approvals of Nouress and another U.S. company’s cysteine hydrochloride injection earlier this year, Avadel expects domestic supply of cysteine hydrochloride injection will be sufficient to support the entire U.S. market, which, under FDA regulations, should preclude further import or U.S. marketing of unapproved cysteine hydrochloride injection products. Under these potential market conditions, the U.S. annual market for cysteine hydrochloride could be greater than $50 million.
https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/L-Cysteine-hydrochloridehttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cysteine
https://www.drugbank.ca/salts/DBSALT001754
FDA Approves Nouress (cysteine hydrochloride) Injection for Treating Neonate Patients Requiring Total Parenteral Nutrition (TPN)