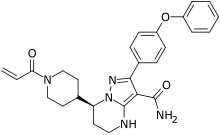
Ceftolozane/tazobactam Tazobactam
Merck (NYSE:MRK), known as MSD outside the United States and Canada, announced that the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved Merck’s supplemental New Drug Application (sNDA) for the use of Zerbaxa (ceftolozane and tazobactam) for the treatment of patients 18 years and older with hospital-acquired bacterial pneumonia and ventilator-associated bacterial pneumonia (HABP/VABP) caused by the following susceptible Gram-negative microorganisms: Enterobacter cloacae, Escherichia coli, Haemophilus influenzae, Klebsiella oxytoca, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Proteus mirabilis, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Serratia marcescens. The sNDA for Zerbaxa had previously been designated Priority Review status by the FDA. To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of Zerbaxa and other antibacterial drugs, Zerbaxa should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by susceptible bacteria.
This expanded use is based on results of the pivotal Phase 3 ASPECT-NP trial that compared Zerbaxa 3g (ceftolozane 2g and tazobactam 1g) intravenously every 8 hours to meropenem (1g intravenously every 8 hours) for 8 to 14 days for the treatment of adult patients with HABP/VABP.
Zerbaxa is contraindicated in patients with known serious hypersensitivity to the components of Zerbaxa (ceftolozane/tazobactam), piperacillin/tazobactam, or other members of the beta-lactam class. Serious and occasionally fatal hypersensitivity (anaphylactic) reactions have been reported in patients receiving beta-lactam antibacterials. Additionally, Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea (CDAD), ranging from mild diarrhea to fatal colitis, has been reported with nearly all systemic antibacterial agents, including Zerbaxa. See Important Safety Information below.
“Pneumonia in ventilated patients remains a significant clinical challenge and is associated with substantial morbidity and mortality,” said Dr. Andrew Shorr, head of pulmonary, critical care and respiratory services, Medstar Washington Hospital Center, Washington, D.C. “The need to cover diverse pathogens including Pseudomonas aeruginosa and certain Enterobacteriaceae adds to the challenge.”
According to a recent publication by the Foundation for the National Institutes of Health Biomarkers Consortium, ventilated patients with HABP have a higher rate of mortality (39%) than those with VABP (27%). In addition, Pseudomonas aeruginosa is the most common Gram-negative pathogen in HABP/VABP and is becoming increasingly difficult to treat.
“We are grateful to all of the patients who participated in the studies which led to the approval of Zerbaxa for the treatment of HABP/VABP,” said Dr. Roy Baynes, senior vice president and head of global clinical development, chief medical officer, Merck Research Laboratories. “This approval reflects Merck’s longstanding commitment to helping alleviate the burden of infectious diseases, including serious infections caused by Gram-negative pathogens.”
Clinical Data Supporting Use of Zerbaxa (Ceftolozane and Tazobactam) in HABP/VABP
A total of 726 adult patients hospitalized with HABP/VABP were enrolled in a multinational, double-blind study (NCT 02070757) comparing Zerbaxa 3g (ceftolozane 2g and tazobactam 1g) intravenously every 8 hours to meropenem (1g intravenously every 8 hours) for 8 to 14 days of therapy. All patients had to be intubated and on mechanical ventilation at randomization.
Efficacy was assessed based on all-cause mortality at Day 28 and clinical cure, defined as complete resolution or significant improvement in signs and symptoms of the index infection at the test-of-cure (TOC) visit which occurred 7 to 14 days after the end of treatment. The analysis population was the intent-to-treat (ITT) population, which included all randomized patients.
Of the 726 patients in the ITT population, the median age was 62 years and 44% of the population was greater than or equal to 65 years of age, with 22% of the population greater than or equal to 75 years of age. The majority of patients were white (83%), male (71%) and were from Eastern Europe (64%). The median APACHE II score was 17 and 33% of patients had a baseline APACHE II score of greater than or equal to 20. All patients were on mechanical ventilation and 519 (71%) had VABP. At randomization, the majority of patients had been hospitalized for greater than or equal to 5 days (77%) and were in an ICU (92%), with 49% of patients ventilated for greater than or equal to 5 days. At baseline, 36% of patients had creatinine clearance (CrCl) less than 80 mL/min. Of these, 14% had CrCl less than 50 mL/min.
Approximately 13% of patients were failing their current antibacterial drug therapy for HABP/VABP, and bacteremia was present at baseline in 15% of patients. Key comorbidities included diabetes mellitus, congestive heart failure, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease at rates of 22%, 16% and 12%, respectively.
Zerbaxa (ceftolozane and tazobactam) was non-inferior to meropenem for 28-day all-cause mortality in the ITT population (all randomized patients), 24.0% (87/362) and 25.3% (92/364) respectively, for a weighted proportion difference of 1.1 (stratified 95% CI: -5.13, 7.39; non-inferiority margin of 10%). In addition, Zerbaxa was non-inferior to meropenem for clinical response at Test-of-Cure (7-14 days after the end of therapy) in the ITT population, 54.4% (197/362) and 53.3% (194/364) respectively, for a weighted proportion difference of 1.1 (stratified 95% CI: -6.17, 8.29; non-inferiority margin of 12.5%).
In the ventilated HABP sub-group, a favorable response for Zerbaxa in 28-day all-cause mortality was observed, 24.2% (24/99) for Zerbaxa and 37.0% (40/108) for meropenem, respectively, for a weighted proportion difference of 12.8 (stratified 95% CI: 0.18, 24.75). In the VABP subgroup, 28-day all-cause mortality was 24.0% (63/263) for Zerbaxa and 20.3% (52/256) for meropenem, for a weighted proportion difference of -3.6 (stratified 95% CI: -10.74, 3.52).
Adverse reactions occurring in 2% or greater of patients receiving Zerbaxa in this study include hepatic transaminase increased 11.9% (43/361), renal impairment/renal failure 8.9% (32/361), diarrhea 6.4% (23/361), intracranial hemorrhage 4.4% (16/361), vomiting 3.3% (12/361), and Clostridium difficile colitis 2.8% (10/361). Treatment discontinuation due to adverse reactions occurred in 1.1% (4/361) of patients receiving Zerbaxa and 1.4% (5/359) of patients receiving meropenem.
FDA Approves Zerbaxa (ceftolozane and tazobactam) 3g Dose for the Treatment of Adults with
Hospital-Acquired and Ventilator-Associated Bacterial Pneumonia (HABP/VABP)







 Solithromycin
Solithromycin