Tuesday, April 6, 2021
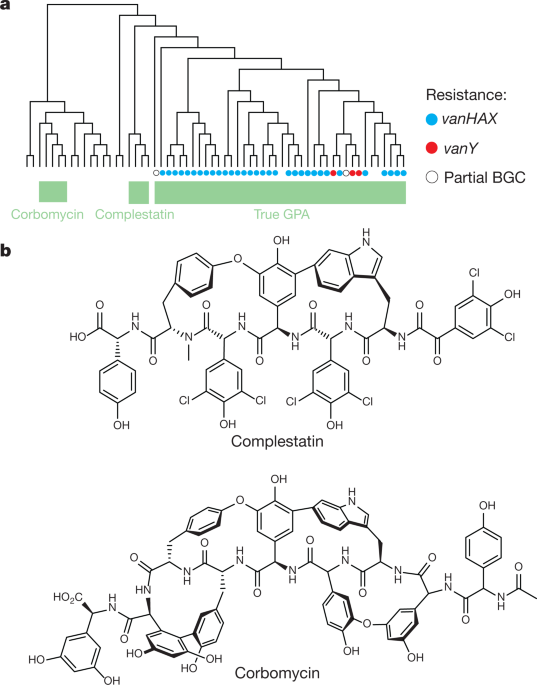
Newly discovered antibiotics kill bacteria differently

Saturday, March 6, 2021
FDA Approves Ukoniq (umbralisib) for Marginal Zone Lymphoma and Follicular Lymphoma
Ukoniq is the first and only, oral, once daily, inhibitor of phosphoinositide 3 kinase (PI3K) delta and casein kinase 1 (CK1) epsilon. Accelerated approval was granted for these indications based on overall response rate (ORR) data from the Phase 2 UNITY-NHL Trial (NCT02793583). Continued approval for these indications may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in a confirmatory trial. This application was granted priority review for the MZL indication. In addition, Ukoniq was granted Breakthrough Therapy Designation (BTD) for the treatment of MZL and orphan drug designation (ODD) for the treatment of MZL and FL.
Michael S. Weiss, Executive Chairman and Chief Executive Officer of TG Therapeutics stated, “Today’s approval of Ukoniq marks a historic day for our Company with this being our first approval and we are extremely pleased to be able to bring our novel inhibitor of PI3K-delta and CK1-epsilon to patients with relapsed/refractory MZL and FL. We have built a commercial team with significant experience who will immediately start to engage our customers to educate them on Ukoniq and how to access the product for patients in need and expect to make Ukoniq available to US distributors in the next few days.” Mr. Weiss continued, “We want to thank the patients, physicians, nurses and clinical coordinators for their support and participation in our clinical trials, and the FDA for their collaboration throughout this process. We remain dedicated to patients with B-cell diseases and our mission of developing treatment options for those in need.”
“Despite treatment advances, MZL and FL remain incurable diseases with limited treatment options for patients who relapse after prior therapy and no defined standard of care. With the approval of umbralisib we now have a targeted, oral, once-daily option, offering a needed treatment alternative for patients,” stated Dr. Nathan Fowler, Professor of Medicine at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center and the Study Chair of the UNITY-NHL MZL &FL cohorts.
“The approval of umbralisib for the treatment of relapsed/refractory marginal zone lymphoma and follicular lymphoma offers patients a new treatment option, and new hope in the fight against these diseases,” stated Meghan Gutierrez, Chief Executive Officer of the Lymphoma Research Foundation.
The safety of Ukoniq monotherapy was based on a pooled population from the 221 adults with MZL and FL in three single arm, open label trials and one open label extension trial. Patients received Ukoniq 800 mg orally once daily. Serious adverse reactions occurred in 18% of patients who received Ukoniq. Serious adverse reactions that occurred in ≥2% of patients were diarrhea-colitis (4%), pneumonia (3%), sepsis (2%), and urinary tract infection (2%). The most common adverse reactions (>15%), including laboratory abnormalities, were increased creatinine (79%), diarrhea-colitis (58%, 2%), fatigue (41%), nausea (38%), neutropenia (33%), ALT increase (33%), AST increase (32%), musculoskeletal pain (27%), anemia (27%), thrombocytopenia (26%), upper respiratory tract infection (21%), vomiting (21%), abdominal pain (19%), decreased appetite (19%), and rash (18%).
Wednesday, March 3, 2021
FDA Approves Tepmetko (tepotinib) as the First and Only Once-daily Oral MET Inhibitor for Patients with Metastatic NSCLC with METex14 Skipping Alterations
EMD Serono, the healthcare business sector of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany in the US and Canada, announced that the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved Tepmetko (tepotinib) following Priority Review for the treatment of adult patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) harboring mesenchymal-epithelial transition (MET) exon 14 skipping alterations. This indication is approved under accelerated approval based on overall response rate and duration of response. Continued approval for this indication may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in confirmatory trials.
The approval is based on results from the pivotal Phase II VISION study evaluating Tepmetko as monotherapy in patients with advanced NSCLC with METex14 skipping alterations.
"METex14 skipping occurs in approximately 3% to 4% of NSCLC cases, and patients with this aggressive lung cancer are often elderly and face a poor clinical prognosis," said Paul K. Paik, M.D., VISION primary investigator and Clinical Director, Thoracic Oncology Service, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center. "There is a pressing need for targeted treatments that have the potential to generate durable anti-tumor activity and improve the lives of patients with this challenging disease. Tepmetko offers an important and welcome new therapeutic option for patients with metastatic NSCLC harboring these genetic mutations."
"In recent years, the treatment of lung cancer has seen powerful progress in the understanding of the genetic mutations that lead to tumor growth, resistance and progression," said Andrea Ferris, President and CEO of LUNGevity. "The availability of a new precision medicine for NSCLC with METex14 skipping alterations advances patient access to targeted treatment and underscores the importance of routine comprehensive biomarker testing for patients with this challenging cancer."
Tepmetko is the first and only FDA approved MET inhibitor that offers once-daily oral dosing and is administered as two 225 mg tablets (450 mg). Patients with metastatic NSCLC should be selected for treatment with Tepmetko based on the presence of MET exon 14 skipping alterations.
"This approval of Tepmetko by the FDA is an important milestone on our mission to significantly improve the treatment of cancer where MET plays a driving role," said Danny Bar-Zohar, M.D., Global Head of Development for the Healthcare business of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany. "Our focus now is to ensure Tepmetko is accessible to patients in the United States and fully integrated into clinical practice given the important advance it represents for indicated patients as an oral once-a-day precision medicine."
EMD Serono, the healthcare business of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany in the US and Canada, is committed to providing patient access and reimbursement support for eligible Tepmetko patients through its Oncology Navigation Center™ (ONC) program in the US. ONC provides a spectrum of patient access and reimbursement support services intended to help US patients receive appropriate treatment access. ONC may be reached at 1-844-662-3631 (844-ONC-EMD1) between 8am-8pm Eastern Time, Monday through Friday, or by visiting OncNavigationCenter.com.
Tepmetko was the first oral MET inhibitor to receive a regulatory approval anywhere in the world for the treatment of advanced NSCLC harboring MET gene alterations, with its approval in Japan in March 2020. The FDA completed its review of Tepmetko under its Real-Time Oncology Review pilot program after previously granting the medicine Breakthrough Therapy Designation. The FDA also recently granted Tepmetko Orphan Drug Designation (ODD).
A Marketing Authorization Application for tepotinib for a similar indication was validated by the European Medicines Agency in November 2020. Applications have also been submitted in Australia, Switzerland, and Canada under the FDA's Project Orbis initiative, which provides a framework for concurrent submission and review of oncology medicines among international partners.1
In the study, Tepmetko demonstrated an overall response rate of 43% (95% CI, 32–56) in treatment-naïve patients (n=69) and 43% (95% CI, 33-55) in previously treated patients (n=83). Median duration of response (DOR) was 10.8 months (95% CI, 6.9-NE) and 11.1 months (95% CI, 9.5-18.5) among treatment-naïve and previously treated patients, respectively. Duration of response of six months or more occurred among 67% of treatment-naïve patients and 75% of previously treated patients, and duration of response of nine months or more occurred among 30% of treatment-naïve patients and 50% of previously treated patients.3
The safety population included 255 patients with NSCLC positive for METex14 skipping alterations, who received Tepmetko in the VISION study. Fatal adverse reactions occurred in one patient (0.4%) due to pneumonitis, one patient (0.4%) due to hepatic failure, and one patient (0.4%) due to dyspnea from fluid overload. Serious adverse reactions occurred in 45% of patients who received Tepmetko. Serious adverse reactions occurring in >2% of patients included pleural effusion (7%), pneumonia (5%), edema (3.9%), dyspnea (3.9%), general health deterioration (3.5%), pulmonary embolism (2%), and musculoskeletal pain (2%). The most common adverse reactions (≥20%) in patients who received Tepmetko were edema, fatigue, nausea, diarrhea, musculoskeletal pain, and dyspnea.
Tuesday, March 2, 2021
FDA Approves Cosela (trilaciclib) to Decrease the Incidence of Chemotherapy-Induced Myelosuppression
G1 Therapeutics, Inc. (Nasdaq: GTHX), a commercial-stage oncology company, announced the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval of Cosela (trilaciclib) for injection to decrease the incidence of chemotherapy-induced myelosuppression in adult patients when administered prior to a platinum/etoposide-containing regimen or topotecan-containing regimen for extensive-stage small cell lung cancer (ES-SCLC). It is the first and only therapy designed to help protect bone marrow (myeloprotection) when administered prior to treatment with chemotherapy. Cosela is expected to be commercially available through G1’s specialty distributor partner network in early March.
“The approval of trilaciclib (Cosela) is an important advance in the treatment of patients with extensive-stage small cell lung cancer receiving chemotherapy,” said Dr. Jeffrey Crawford, Geller Professor for Research in Cancer in the Department of Medicine and Duke Cancer Institute. “The most serious and life-threatening side effect of chemotherapy is myelosuppression, or damage to the bone marrow, resulting in reduced white blood cells, red blood cells and platelets. Chemotherapy-induced myelosuppression may lead to increased risks of infection, severe anemia, and/or bleeding. These complications impact patients’ quality of life and may also result in chemotherapy dose reductions and delays. To date, approaches have included the use of growth factor agents to accelerate blood cell recovery after the bone marrow injury has occurred, along with antibiotics and transfusions as needed. By contrast, trilaciclib provides the first proactive approach to myelosuppression through a unique mechanism of action that helps protect the bone marrow from damage by chemotherapy. In clinical trials, the addition of trilaciclib to extensive-stage small cell lung cancer chemotherapy treatment regimens reduced myelosuppression and improved clinical outcomes. The good news is that these benefits of trilaciclib will now be available for our patients in clinical practice.”
Chemotherapy is an effective and important weapon against cancer. However, chemotherapy does not differentiate between healthy cells and cancer cells. It kills both, including important hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSPCs) in the bone marrow that produce white blood cells (immune cells that help fight infection), red blood cells (cells that carry oxygen from the lungs to the tissues), and platelets (cells that prevent bleeding from cancer, surgeries, chronic diseases, and injuries). This chemotherapy-induced bone marrow damage, known as myelosuppression, can lead to increased risk of infection, anemia, thrombocytopenia, and other complications. Myeloprotection is a novel approach of protecting HSPCs in the bone marrow from chemotherapy-induced damage. This approach can help reduce some chemotherapy-related toxicity, making chemotherapy safer and more tolerable, while also reducing the need for reactive rescue interventions.
“Chemotherapy is the most effective and widely used approach to treating people diagnosed with extensive-stage small cell lung cancer; however, standard of care chemotherapy regimens are highly myelosuppressive and can lead to costly hospitalizations and rescue interventions,” said Jack Bailey, Chief Executive Officer at G1 Therapeutics. “Cosela will help change the chemotherapy experience for people who are battling ES-SCLC. G1 is proud to deliver Cosela to patients and their families as the first and only therapy to help protect against chemotherapy-induced myelosuppression.”
Cosela is administered intravenously as a 30-minute infusion within four hours prior to the start of chemotherapy and is the first FDA-approved therapy that helps provide proactive, multilineage protection from chemotherapy-induced myelosuppression. The approval of Cosela is based on data from three randomized, placebo-controlled trials that showed patients receiving Cosela prior to the start of chemotherapy had clinically meaningful and statistically significant reduction in the duration and severity of neutropenia. Data also showed a positive impact on red blood cell transfusions and other myeloprotective measures. The trials evaluated Cosela in combination with carboplatin/etoposide (+/- the immunotherapy atezolizumab) and topotecan chemotherapy regimens. Approximately 90% of all patients with ES-SCLC will receive at least one of these regimens during the course of their treatment.
The majority of adverse reactions reported with Cosela were mild to moderate in severity. The most common adverse reactions (≥10%) were fatigue, hypocalcemia, hypokalemia, hypophosphatemia, aspartate aminotransferase increased, headache, and pneumonia. Serious adverse reactions occurred in 30% of patients receiving Cosela. Serious adverse reactions reported in >3% of patients who received Cosela included respiratory failure, hemorrhage, and thrombosis. Grade 3/4 hematological adverse reactions occurring in patients treated with Cosela and placebo included neutropenia (32% and 69%), febrile neutropenia (3% and 9%), anemia (16% and 34%), thrombocytopenia (18% and 33%), and leukopenia (4% and 17%), respectively.
“Quite often, people diagnosed with extensive-stage small cell lung cancer rely on chemotherapy to not only extend their lives, but also to acutely alleviate their symptoms,” said Bonnie J. Addario, lung cancer survivor, co-founder and board chair of the Go2 Foundation for Lung Cancer. “Unfortunately, the vast majority will experience chemotherapy-induced side effects, resulting in dose delays and reductions, and increased utilization of healthcare services. G1 shares our organization’s goal to improve the quality of life of those diagnosed with lung cancer and to transform survivorship among people living with this insidious disease. We are thrilled to see new advancements that can help improve the lives of those living with small cell lung cancer.”
Approximately 30,000 small cell lung cancer patients are treated in the United States annually. G1 is committed to helping patients with extensive-stage small cell lung cancer in the U.S. gain access to treatment with Cosela. For more information on access and affordability programs, patients and providers should call the G1toOne support center at 833-G1toONE (833-418-6663) from 8:00 a.m. to 8:00 p.m. Eastern time.
G1 received Breakthrough Therapy Designation from the FDA in 2019 based on positive data in small cell lung cancer patients from three randomized Phase 2 clinical trials. As is common with breakthrough-designated products that receive priority review, G1 will conduct certain post-marketing activities, including in vitro drug-drug interaction and metabolism studies, and a clinical trial to assess impact of trilaciclib on disease progression or survival in patients with ES-SCLC with chemotherapy-induced myelosuppression treated with a platinum/etoposide-containing or topotecan-containing regimen with at least a two year follow up. G1 intends to initiate the post-approval clinical trial in 2022.
Cosela (trilaciclib) Co-Promotion Agreement with Boehringer Ingelheim
In June 2020, G1 announced a three-year co-promotion agreement with Boehringer Ingelheim for Cosela in small cell lung cancer in the U.S. and Puerto Rico. G1 will lead marketing, market access and medical engagement initiatives for Cosela. The Boehringer Ingelheim oncology commercial team, well-established in lung cancer, will lead sales force engagement initiatives. G1 will book revenue and retain development and commercialization rights to Cosela and pay Boehringer Ingelheim a promotional fee based on net sales. The three-year agreement does not extend to additional indications that G1 is evaluating for trilaciclib. Press release details of the G1/ Boehringer Ingelheim agreement can be found here.
Thursday, January 28, 2021
Alzheimer's disease drug may help fight against antibiotic resistance
In continuation of my update on PBT2
Researchers from The University of Queensland, The University of Melbourne and Griffith University have discovered that the drug called PBT2 is effective at disrupting and killing a class of bacteria -- known as Gram-negative bacteria -- that cause infections such as pneumonia, bloodstream infections and meningitis.
UQ's Professor Mark Walker said the metal transport drug may offer a last line of defence against some of the world's most difficult to treat superbugs.
"The emergence of antibiotic-resistant superbugs is an urgent threat to human health, undermining the capacity to treat patients with serious infection," Professor Walker said.
"Alternative strategies to treat such multi-drug resistant bacteria are urgently needed.
"Led by UQ's Dr David De Oliveira, our team hypothesised that, by using this experimental Alzheimer's treatment to disrupt the metals inside these bacteria, we would also disrupt their mechanisms of antibiotic resistance.
"This was shown to be the case, with the Alzheimer's drug -- combined with the antibiotic polymyxin -- successfully tackling antibiotic-resistant superbugs like Klebsiella pneumoniae, Acinetobacter baumannii, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Escherichia coli."
Griffith University's Professor Mark von Itzstein AO from the Institute for Glycomics said the new treatment was effective, and offered a range of other benefits.
"Based on its use as an experimental Alzheimer's treatment, there's been a significant amount of solid science done on this drug already," Professor von Itzstein said.
"We know, for example, that clinical studies of PBT2 show that it is safe for use in humans.
"And, given that we've been able to combine it with the antibiotic polymyxin to treat polymyxin-resistant bacteria, we may be able to make other now-ineffective antibiotics become effective again for treating infectious diseases.
"This could resharpen, so to speak, some of the weapons we thought we'd lost in our fight against antibiotic-resistant bacteria."
The University of Melbourne's Associate Professor Christopher McDevitt, from the Peter Doherty Institute for Infection and Immunity (Doherty Institute), said the drug had already proved effective beyond the petri dish.
"Animal studies show that the combination of polymyxin and PBT2 kills polymyxin-resistant bacteria, completely clearing any infection," Associate Professor McDevitt said.
"Hopefully in the not-too-distant future people will be able to access this type of treatment in the clinic.
"New techniques are critical in addressing this building threat to human health, and this treatment is an additional weapon in our arsenal to fight the accelerating threat of antibiotic resistance.
"If these new solutions aren't developed, it's estimated that by 2050, antimicrobial-resistant bacteria will account for more than 10 million deaths per year.
"This new treatment could help turn the tide on antibiotic resistance."
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/PBT2
Wednesday, December 30, 2020
FDA Approves Evrysdi (risdiplam) for Treatment of Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA) in Adults and Children 2 Months and Older
Genentech, a member of the Roche Group, announced the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval of Evrysdi (risdiplam) for treatment of spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) in adults and children 2 months of age and older. Evrysdi showed clinically-meaningful improvements in motor function across two clinical trials in people with varying ages and levels of disease severity, including Types 1, 2, and 3 SMA. Infants achieved the ability to sit without support for at least 5 seconds, a key motor milestone not normally seen in the natural course of the disease. Evrysdi also improved survival without permanent ventilation at 12 and 23 months, compared to natural history. A liquid medicine, Evrysdi is administered daily at home by mouth or feeding tube.
“Given the majority of people with SMA in the U.S. remain untreated, we believe Evrysdi, with its favorable clinical profile and oral administration, may offer meaningful benefits for many living with this rare neurological disease,” said Levi Garraway, M.D., Ph.D., chief medical officer and head of Global Product Development. “The strength and resolve of the SMA community has continually inspired us as we developed this first-of-its-kind medicine for SMA, so today we celebrate our collective accomplishment together with them.”
Evrysdi is being studied in more than 450 people as part of a large and robust clinical trial program in SMA. The program includes infants aged 2 months to adults aged 60 with varying symptoms and motor function, such as people with scoliosis or joint contractures, and those previously treated for SMA with another medication. The approval is based on data from two clinical studies designed to represent a broad spectrum of people living with SMA: FIREFISH in symptomatic infants aged 2 to 7 months; and SUNFISH in children and adults aged 2 to 25 years. SUNFISH is the first and only placebo-controlled trial to include adults with Types 2 and 3 SMA.
In FIREFISH, 41% (7/17) of infants treated with the therapeutic dose achieved the ability to sit without support for at least 5 seconds as measured by the Bayley Scales of Infant and Toddler Development Third Edition (BSID-III). Additionally, 90% (19/21) of infants were alive without permanent ventilation at 12 months of treatment and reached 15 months of age or older. As described in the natural history of untreated infantile-onset SMA, infants would not be expected to be able to sit independently, and only 25% would be expected to survive without permanent ventilation beyond 14 months of age. In SUNFISH, children and adults treated with Evrysdi experienced a clinically-meaningful and statistical-significant improvement in motor function at 12 months (1.55 point mean difference; p=0.0156) compared to placebo (1.36 points [95% CI: 0.61, 2.11]; -0.19 points [95% CI: -1.22, 0.84], respectively), as measured by a change from baseline in the Motor Function Measure-32 (MFM-32) total score.
Evrysdi demonstrated a favorable efficacy and safety profile, with the safety profile established across the FIREFISH and SUNFISH trials. The most common adverse reactions were fever, diarrhea, and rash in later-onset SMA. In infantile-onset SMA, the most common adverse events were similar and also included upper respiratory tract infection, pneumonia, constipation, and vomiting. There were no treatment-related safety findings leading to withdrawal from either study.
“Throughout their lives, many people with SMA may lose their ability to perform critical movements, which can impact the ability to independently participate in aspects of daily life and even be life altering,” said Kenneth Hobby, president of Cure SMA. “The approval of Evrysdi is an eagerly awaited milestone for our community. We appreciate Genentech’s commitment to reflecting the full scope of the real-world SMA population in their clinical trial program and developing a treatment that can be administered at home.”
Evrysdi is designed to treat SMA by increasing production of the survival of motor neuron (SMN) protein. SMN protein is found throughout the body and is critical for maintaining healthy motor neurons and movement. Genentech leads the clinical development of Evrysdi as part of a collaboration with the SMA Foundation and PTC Therapeutics.
Evrysdi will be available in the United States within two weeks for direct delivery to patients’ homes through Accredo Health Group Inc., an Express Scripts specialty pharmacy.
Genentech is committed to helping patients access the medicines prescribed by their physician. For people with SMA, the MySMA Support program team is available to answer questions, provide product education and help families understand insurance coverage and navigate appropriate financial assistance options to start and stay on Evrysdi. Patients can call 1-833-EVRYSDI or visit http://www.Evrysdi.com or https://www.Genentech-Access.com to learn more.
Monday, December 14, 2020
Fluvoxamine may prevent serious illness in COVID-19 patients, study suggests: Antidepressant drug repurposed for patients with coronavirus infection
The study, a collaboration between the university's Department of Psychiatry and Division of Infectious Diseases, involved 152 patients infected with SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19. Researchers compared the outcomes of those treated with fluvoxamine to the outcomes of those given an inactive placebo. After 15 days, none of the 80 patients who had received the drug experienced serious clinical deterioration. Meanwhile, six of the 72 patients given placebo (8.3%) became seriously ill, with four requiring hospitalization.
The study is published online Nov. 12 in the Journal of the American Medical Association.
"The patients who took fluvoxamine did not develop serious breathing difficulties or require hospitalization for problems with lung function," said the paper's first author, Eric J. Lenze, MD, the Wallace and Lucille Renard Professor of Psychiatry. "Most investigational treatments for COVID-19 have been aimed at the very sickest patients, but it's also important to find therapies that prevent patients from getting sick enough to require supplemental oxygen or to have to go to the hospital. Our study suggests fluvoxamine may help fill that niche."
Fluvoxamine is used commonly to treat obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), social anxiety disorder and depression. It is in a class of drugs known as selective serotonin-reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), but unlike other SSRIs, fluvoxamine interacts strongly with a protein called the sigma-1 receptor. That receptor also helps regulate the body's inflammatory response.
"There are several ways this drug might work to help COVID-19 patients, but we think it most likely may be interacting with the sigma-1 receptor to reduce the production of inflammatory molecules," said senior author Angela M Reiersen, MD, an associate professor of psychiatry. "Past research has demonstrated that fluvoxamine can reduce inflammation in animal models of sepsis, and it may be doing something similar in our patients."
Reiersen said the drug's effects on inflammation could prevent the immune system from mounting an overwhelming response, which is thought to occur in some COVID-19 patients who seem to improve after a few days of illness and then worsen. Many of those patients end up hospitalized, and some die.
In an innovative twist to research during the pandemic, the study was conducted remotely. When a symptomatic patient tested positive and enrolled in the study, research staff delivered the medication or inactive placebo to them, along with thermometers, automatic blood pressure monitors and fingertip oxygen sensors.
"Our goal is to help patients who are initially well enough to be at home and to prevent them from getting sick enough to be hospitalized," said Caline Mattar, MD, an assistant professor of medicine in the Division of Infectious Diseases. "What we've seen so far suggests that fluvoxamine may be an important tool in achieving that goal."
For two weeks, subjects took either the antidepressant drug or placebo sugar pills while having daily interactions with members of the research team -- via phone or computer. That allowed patients to report on their symptoms, oxygen levels and other vital signs. If patients suffered shortness of breath or were hospitalized for pneumonia, or their oxygen saturation levels fell below 92%, their conditions were considered to have deteriorated.
"The good news is that not a single person taking the active medication experienced deterioration," Reiersen said. "We believe this drug may be the reason, but we need to study more patients to make sure."
The researchers will begin a larger study in the next few weeks. Lenze, the director of the Healthy Mind Lab at the School of Medicine, is an expert in using mobile and internet technology to conduct clinical trials. He said that although this initial study involved patients in the St. Louis region, the next phase of the research will involve patients from throughout the country.
"We bring the study to the patients, giving them tools to monitor their health at home," Lenze said. "Our hope is that we can keep these patients healthy enough to avoid hospitalization."
This work was supported by the Taylor Family Institute for Innovative Psychiatric Research, the Bantly Foundation, the Center for Brain Research in Mood Disorders at Washington University and the COVID-19 Early Treatment Fund. Additional support from the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences of the National Institutes of Health (NIH). Grant number UL1 TR002345.
Monday, July 6, 2020
Experimental Antiviral Drug to Be Tested Against New Coronavirus
Tuesday, March 3, 2020
FDA Approves Fetroja (cefiderocol) for the Treatment of Complicated Urinary Tract Infections

“Today’s approval provides an additional treatment option for patients with cUTIs who have limited or no alternative treatment options,” said John Farley, M.D., M.P.H., acting director of the Office of Infectious Diseases in the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research. “A key global challenge the FDA faces as a public health agency is addressing the threat of antimicrobial-resistant infections, like cUTIs. This approval represents another step forward in the FDA’s overall efforts to ensure safe and effective antimicrobial drugs are available to patients for treating infections.”
Monday, March 2, 2020
FDA Approves Brukinsa (zanubrutinib) for the Treatment of Mantle Cell Lymphoma
“We are working to improve outcomes for people with cancer worldwide and this approval brings us closer to realizing our mission of bringing the highest quality therapies to patients globally,” said John V. Oyler, Chairman, Co-Founder, and CEO of BeiGene. “Today’s FDA approval of Brukinsa, following the previously granted Breakthrough Therapy designation in this indication, validates it as an important treatment option for people with relapsed or refractory MCL. We hope this is the first of many approvals for Brukinsa as we continue to evaluate its potential in other hematologic cancers.”
“Brukinsa is a BTK inhibitor that was designed to maximize target occupancy and minimize off-target binding. It entered the clinic in 2014 and since that time our broad development program has enrolled more than 1,600 patients globally,” said Jane Huang, M.D., Chief Medical Officer, Hematology at BeiGene. “Today’s accelerated approval is the culmination of many years of effort by the BeiGene team, the dedicated investigators involved in these trials and, most importantly, the patients who participated by enrolling in the clinical trials. We are humbled by the opportunity to develop this therapy and launch it as our first internally discovered and approved cancer treatment.”
“BTK inhibition is an established mode of treatment for patients with MCL, but many patients treated with previously approved BTK inhibitors do not fully respond to BTK therapy or are forced to discontinue treatment early due to side effects. Today we have a new option for our adult patients who have received one prior systemic or targeted therapy and are living with MCL, an aggressive blood cancer that’s often diagnosed at a more advanced stage,” said Luhua (Michael) Wang, M.D., Professor, Department of Lymphoma and Myeloma, Division of Cancer Medicine at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, and clinical trial investigator.
“The approval of Brukinsa as a second line therapy represents an important advancement for the treatment of mantle cell lymphoma,” said Meghan Gutierrez, Chief Executive Officer for the Lymphoma Research Foundation. “Expanded treatment options can transform the patient experience and provide hope to people living with a mantle cell diagnosis.”
Tuesday, February 25, 2020
FDA Approves Brukinsa (zanubrutinib) for the Treatment of Mantle Cell Lymphoma

“We are working to improve outcomes for people with cancer worldwide and this approval brings us closer to realizing our mission of bringing the highest quality therapies to patients globally,” said John V. Oyler, Chairman, Co-Founder, and CEO of BeiGene. “Today’s FDA approval of Brukinsa, following the previously granted Breakthrough Therapy designation in this indication, validates it as an important treatment option for people with relapsed or refractory MCL. We hope this is the first of many approvals for Brukinsa as we continue to evaluate its potential in other hematologic cancers.”
“Brukinsa is a BTK inhibitor that was designed to maximize target occupancy and minimize off-target binding. It entered the clinic in 2014 and since that time our broad development program has enrolled more than 1,600 patients globally,” said Jane Huang, M.D., Chief Medical Officer, Hematology at BeiGene. “Today’s accelerated approval is the culmination of many years of effort by the BeiGene team, the dedicated investigators involved in these trials and, most importantly, the patients who participated by enrolling in the clinical trials. We are humbled by the opportunity to develop this therapy and launch it as our first internally discovered and approved cancer treatment.”
“BTK inhibition is an established mode of treatment for patients with MCL, but many patients treated with previously approved BTK inhibitors do not fully respond to BTK therapy or are forced to discontinue treatment early due to side effects. Today we have a new option for our adult patients who have received one prior systemic or targeted therapy and are living with MCL, an aggressive blood cancer that’s often diagnosed at a more advanced stage,” said Luhua (Michael) Wang, M.D., Professor, Department of Lymphoma and Myeloma, Division of Cancer Medicine at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, and clinical trial investigator.
“The approval of Brukinsa as a second line therapy represents an important advancement for the treatment of mantle cell lymphoma,” said Meghan Gutierrez, Chief Executive Officer for the Lymphoma Research Foundation. “Expanded treatment options can transform the patient experience and provide hope to people living with a mantle cell diagnosis.”
The FDA’s approval of Brukinsa is based on efficacy results from two single-arm clinical trials, with independent review committee (IRC)-assessed ORR per 2014 Lugano Classification as the primary endpoint. Across both trials, Brukinsa achieved an ORR, which is the sum of complete responses and partial responses, of 84%.






