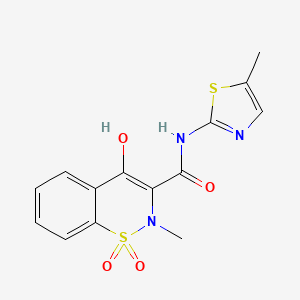
Clovis Oncology, Inc. announced that the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved Rubraca (rucaparib) tablets for the maintenance treatment of adult patients with recurrent epithelial ovarian, fallopian tube, or primary peritoneal cancer who are in a complete or partial response to platinum-based chemotherapy. FDA granted regular approval for Rubraca in this second, broader and earlier-line indication on a priority review timeline based on positive data from the phase 3 ARIEL3 clinical trial. Biomarker testing is not required for patients to be prescribed Rubraca in this maintenance treatment indication. Warnings and precautions include Myelodysplastic Syndrome (MDS), Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML), and embryo-fetal toxicity.
In addition to granting Rubraca approval in this second indication, the FDA converted the approval of the initial treatment indication from accelerated to regular approval.
“Rubraca provided statistically-significant improvement in PFS versus placebo to all patients, regardless of BRCA mutation status,” said Robert L. Coleman, MD, Professor & Executive Director, Cancer Network Research, Ann Rife Cox Chair in Gynecology, Department of Gynecologic Oncology and Reproductive Medicine at University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston and one of the Principal Investigators in the ARIEL3 clinical trial program. “Both the efficacy and safety results from the ARIEL3 study reinforce the important role of Rubraca in the treatment of recurrent ovarian cancer and expands the treatment options for patients and physicians battling this disease.”
“This FDA approval provides a meaningful advancement for the treatment of women with recurrent ovarian cancer, offering them the potential to reduce their risk of disease progression following platinum-based chemotherapy,” said Patrick J. Mahaffy, CEO and President of Clovis Oncology. “We are grateful that the FDA expedited review of this maintenance treatment indication, so that physicians can begin offering it to appropriate patients beginning today.”
On February 28, 2018, Rubraca was added to the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology Ovarian Cancer, as maintenance therapy for patients with platinum-sensitive epithelial ovarian, fallopian tube and primary peritoneal cancer who are in partial or complete response after completion of two or more lines of platinum-based therapy. The NCCN designated Rubraca as a category 2A treatment.
NCCN is a not-for-profit alliance that includes 27 of the world’s leading cancer institutions. The NCCN Guidelines document evidence-based, consensus-driven management to ensure that all patients receive preventive, diagnostic, treatment, and supportive services that are most likely to lead to optimal outcomes.[1]
In December 2017, FDA accepted the Rubraca supplemental New Drug Application (sNDA) application and granted priority review status. Priority review designation is granted to proposed medicines that FDA has determined have the potential, if approved, to offer a significant improvement in the safety or effectiveness for the treatment, prevention or diagnosis of a serious condition when compared to standard applications. The Rubraca maintenance treatment approval is based on positive results from the ARIEL3 study, which evaluated Rubraca in the ovarian cancer maintenance-treatment setting among three populations: 1) BRCA mutant (BRCAmut+) 2) HRD positive inclusive of BRCAmut+ and, 3) all patients treated in ARIEL3. The study enrolled a total of 564 patients.
ARIEL3 successfully achieved both its primary and key secondary endpoints, extending investigator assessed progression-free survival (PFS) versus placebo in all patients treated, regardless of BRCA status.
Clovis announced topline results from the ARIEL3 clinical trial in June 2017. Additional data from the trial were presented at the 2017 European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) Annual Conference in Madrid, Spain, and subsequently published in The Lancet.
“The FDA approval of Rubraca in the maintenance treatment setting is an important milestone for physicians and their patients with recurrent ovarian cancer because it offers them greater flexibility to use this novel PARP inhibitor, which has demonstrated significant clinical efficacy and has been well received in practice,” said Professor Jonathan Ledermann, MD, Professor of Medical Oncology, Clinical Director, UCL Cancer Institute, and European and the rest of world Principal Investigator for the ARIEL3 study. “This will enable physicians to offer Rubraca to more women with platinum-sensitive, recurrent ovarian cancer.”
"Tens of thousands of women will battle ovarian cancer every year,” said David Barley, Chief Executive Officer, National Ovarian Cancer Coalition. “We need therapies that provide clinically meaningful improvements in reducing the risk of disease progression, among women with recurrent disease."
The safety evaluation of Rubraca 600 mg twice daily as monotherapy for maintenance treatment is based on data from 561 patients with recurrent ovarian cancer treated in the ARIEL3 trial. The safety and tolerability of Rubraca observed in this study was consistent with the previous Rubraca studies. The most common adverse reactions (greater than or equal to 20% of patients; CTCAE Grade 1-4) were nausea, fatigue/asthenia, abdominal pain/distention, rash, dysgeusia, anemia, AST/ALT elevation, constipation, vomiting, diarrhea, thrombocytopenia, nasopharyngitis/upper respiratory tract infection, stomatitis, decreased appetite and neutropenia. The most common laboratory abnormalities (greater than or equal to 25% of patients; CTCAE Grade 1-4) were increase in creatinine, decrease in hemoglobin, increase in cholesterol, increase in alanine aminotransferase (ALT), increase in increase in aspartate aminotransferase (AST), decrease in platelets, decrease in leukocytes, decrease in neutrophils, increase in alkaline phosphatase and decrease in lymphocytes. The majority of adverse reactions and laboratory abnormalities were Grade 1-2.