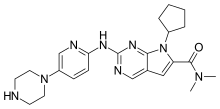
The addition of the CDK4/6 inhibitor ribociclib to letrozole therapy significantly improves progression-free survival in postmenopausal women with hormone receptor-positive advanced breast cancer, researchers reported today at the ESMO 2016 Congress in Copenhagen.
The first interim analysis of data from the randomized, double-blind MONALEESA study showed a 44% improvement in progression-free survival with ribociclib plus letrozole as a first-line treatment combination.
"This was THE definitive study to demonstrate the superiority of the combination of ribociclib and letrozole over letrozole alone," said principle investigator, Professor Gabriel Hortobagyi, from the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston, Texas, US.
Researchers randomized 668 postmenopausal women with hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative advanced breast cancer, who had not undergone any prior systemic treatment, to ribociclib (600 mg/day, 3 weeks on/1 week off) and letrozole (2.5 mg/day, continuous), or letrozole plus placebo.
ribociclib letrozole
In the ribociclib arm, there was a 44% improvement in the primary objective of progression-free survival compared to the placebo arm (HR: 0.556, p = 0.00000329). Median progression-free survival was 14.7 months in the placebo arm, but was not reached in the ribociclib arm at data cut-off.
"The results of this trial represent a compelling proof of principle, and suggest a paradigm shift in metastatic, HR+ breast cancer. They also suggest that testing combinations of ribociclib with other inhibitors of various signaling pathways might lead to additional progress in the management of several subtypes of breast cancer," Hortobagyi said.
Patients with measurable disease at baseline showed a significantly higher objective response rate to ribociclib plus letrozole compared to letrozole alone (53% vs. 37%; p=0.00028), and improved clinical benefit rate (80% vs. 72% p=0.02).
Serious adverse events occurred in fewer than 5% of patients in both arms but other adverse events were significantly more common in the ribociclib arm. Neutropenia occurred in 59% of patients in the ribociclib arm compared to 1% of the placebo arm; leukopenia occurred in 21% vs 1%; lymphopenia in 7% vs. 1%, and patients in the ribociclib arm had a higher incidence of elevated alanine aminotransferase and elevated aspartate aminotransferase.
The number of deaths in the study was too low to enable a reliable analysis of the impact of ribociclib therapy on overall survival.
Commenting on the findings, Professor Giuseppe Curigliano, Director of the New Drugs and Early Drug Development for Innovative Therapies Division at the European Institute of Oncology, Milan, Italy, said, "I believe the results of this study are significant because now we have a new CDK4/6 inhibitor for patients with estrogen-receptor positive metastatic breast cancer, in addition to palbociclib (already FDA approved) and abemaciclib (under development)."
"The addition of ribociclib to letrozole does increase the rate of toxicity, but overall, if we evaluate the magnitude of clinical benefit, there is definitely a benefit to be gained from adding ribociclib."
Curigliano also suggested that further studies of ribociclib should examine the use of cancer biomarkers to better identify patients who would respond to the combination.