Farr cautioned that the experiment was conducted in a mouse model. Like any drug, before an antisense compound could be tested in human clinical trials, toxicity tests need to be completed.
Antisense is a strand of molecules that bind to messenger RNA, launching a cascade of cellular events that turns off a certain gene.
In this case, OL-1 blocks the translation of RNA, which triggers a process that keeps excess amyloid beta protein from being produced. The specific antisense significantly decreased the over expression of a substance called amyloid beta protein precursor, which normalized the amount of amyloid beta protein in the body. Excess amyloid beta protein is believed to be partially responsible for the formation of plaque in
the brain of patients who have Alzheimer's disease.
Scientists tested OL-1 in a type of mouse that overexpresses a mutant form of the human amyloid beta precursor gene. Previously they had tested the substance in a mouse model that has a natural mutation causing it to overproduce mouse amyloid beta. Like people who have Alzheimer's disease, both types of mice have age-related impairments in learning and memory, elevated levels of amyloid beta protein that stay in the brain and increased inflammation and oxidative damage to the hippocampus the part of the brain responsible for learning and memory.
"To be effective in humans, OL-1 would need to be effective at suppressing production of human amyloid beta protein," Farr said.
Scientists compared the mice that were genetically engineered to overproduce human amyloid beta protein with a wild strain, which served as the control. All of the wild strain received random antisense, while about half of the genetically engineered mice received random antisense and half received OL-1.
The mice were given a series of tests designed to measure memory, learning and appropriate behavior, such as going through a maze, exploring an unfamiliar location and recognizing an object.
Scientists found that learning and memory improved in the genetically engineered mice that received OL-1 compared to the genetically engineered mice that received random antisense. Learning and memory were the same among genetically engineered mice that received OL-1 and wild mice that received random antisense.
They also tested the effect of administering the drug through the central nervous system, so it crossed the blood brain barrier to enter the brain directly, and of giving it through a vein in the tail, so it circulated through the bloodstream in the body. They found where the drug was injected had little effect on learning and memory.
Ref http://iospress.metapress.com/content/px72758w0158103u/?issue=4&genre=article&spage=1005&issn=1387-2877&volume=40


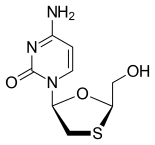




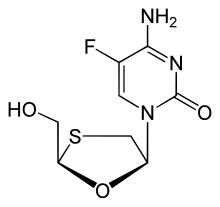 Emtricitabine
Emtricitabine  Rilpivirine
Rilpivirine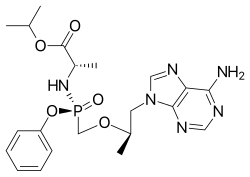 Tenofovir alafenamide
Tenofovir alafenamide

