In continuation of my update on abemaciclib
Eli Lilly and Company (NYSE: LLY) announced the results from the MONARCH 1 Phase 2 study of abemaciclib, a cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) 4 and CDK 6 inhibitor, in patients with hormone-receptor-positive (HR+), human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative (HER2-) metastatic breast cancer. The data, which were presented at the 2016 American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) Annual Meeting by Maura Dickler, M.D., of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, showed that single-agent activity was observed in metastatic breast cancer patients, for whom endocrine therapy was no longer a suitable treatment option. The MONARCH 1 results (abstract #510) confirmed objective response (ORR), durability of response (DoR), clinical benefit rate (CBR) and progression-free survival (PFS).
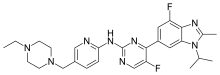 abemaciclib
abemaciclib
The single-arm study, designed to evaluate the safety and efficacy of abemaciclib monotherapy, enrolled 132 patients who were given 200 mg of abemaciclib orally every 12 hours until disease progression. Patients enrolled in the study were heavily pretreated, having experienced progressive disease on or after prior endocrine therapy, and had received prior chemotherapy with one or two chemotherapy regimens for metastatic disease. The primary objective of the trial was investigator-assessed ORR, with secondary endpoints of DoR, CBR and PFS.
"After endocrine therapies are no longer considered appropriate for HR+ metastatic breast cancer patients, when the disease is refractory or aggressive, chemotherapy is the only option. The side effects can be distressing and may be long lasting, limiting the options for patients," said José Baselga, M.D., Ph.D., physician-in-chief and chief medical officer, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, and senior study author. "To see this level of anti-tumor activity, combined with the toxicity profile observed in MONARCH 1, is compelling."
At the final analysis of response (minimum of 12 months follow-up), patients treated with abemaciclib achieved an ORR of 19.7 percent (95% confidence interval (CI): 13.3 – 27.5%), with a median time to response of 3.7 months and a median DoR of 8.6 months. The median PFS was six months with a CBR (defined as patients who achieved complete response, partial response or stable disease for six months or longer) of 42.4 percent. Of the 13 patients who remained on treatment at the time of this analysis, nine were responders and four had stable disease (SD).
"In this population of heavily pretreated patients with a particularly poor prognosis, abemaciclib has shown promising single agent activity and tolerability," said Richard Gaynor, M.D., senior vice president, product development and medical affairs for Lilly Oncology. "These data reinforce our belief in abemaciclib as a potential best-in-class CDK 4 and CDK 6 inhibitor and add to the growing body of evidence that sustained target inhibition can lead to improved patient outcomes."
The safety and toxicity profile of twice daily, continuously dosed abemaciclib was consistent with previous Phase 1 experience. The most common grade 3 non-laboratory treatment emergent adverse events (AEs) were diarrhea (19.7%) and fatigue (12.9%), with no grade 4 non-laboratory events reported. The most common laboratory AEs were neutropenia (22.3% grade 3, 4.6% grade 4) and leukopenia (27.4% grade 3) in this population; 7.6 percent of patients discontinued treatment due to AEs, one due to diarrhea.
Beyond MONARCH 1, Lilly has an active clinical development program studying abemaciclib in breast cancer. Abemaciclib is being evaluated in two Phase 3 clinical trials: MONARCH 2 to evaluate the combination of abemaciclib and fulvestrant for treatment of HR+, HER2- advanced or metastatic breast cancer in postmenopausal women, and MONARCH 3 to evaluate the combination of abemaciclib and a nonsteroidal aromatase inhibitor in HR+, HER2- locoregionally recurrent or metastatic breast cancer in postmenopausal women.
Lilly plans to publish further data from the MONARCH 1 trial later this year.
About Metastatic Breast Cancer
Breast cancer is the most common cancer in women worldwide with nearly 1.7 million new cases diagnosed in 2012.1 In the U.S. this year, approximately 246,660 new cases of invasive breast cancer will be diagnosed and about 40,450 people will die from breast cancer.2 Of all early stage breast cancer cases diagnosed in the U.S., approximately 30 percent will become metastatic, spreading to other parts of the body. In addition, an estimated six to 10 percent of all new breast cancer cases are initially diagnosed as being stage IV, or metastatic.3 Metastatic breast cancer is considered incurable, but is generally treatable.
About Abemaciclib
Abemaciclib (LY2835219) is an investigational, oral cell cycle inhibitor, designed to block the growth of cancer cells by specifically inhibiting cyclin-dependent kinases, CDK 4 and CDK 6. In many cancers, uncontrolled cell growth arises from a loss of cell cycle regulation due to increased signaling from CDK 4 and CDK 6. Abemaciclib inhibits both CDK 4 and CDK 6, and was shown in cell-free enzymatic assays to be most active against Cyclin D 1 and CDK 4.
In 2015, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration granted abemaciclib Breakthrough Therapy Designation based on data from the breast cancer cohort expansion of the company's Phase 1 trial, JPBA, which studied the efficacy and safety of abemaciclib in women with advanced or metastatic breast cancer. In addition to its current MONARCH clinical trials evaluating abemaciclib in breast cancer, a Phase 3 trial of abemaciclib in lung cancer is also underway.

 phentermine
phentermine 
 lorcaserin
lorcaserin Bupropion/naltrexone
Bupropion/naltrexone