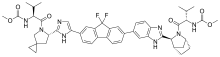
In continuation of my updates on palbociclib

Pfizer Inc. (NYSE:PFE) announced that the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved a new indication expanding the use of Ibrance (palbociclib) 125mg capsules, Pfizer’s metastatic breast cancer therapy. Now Ibrance also is approved for the treatment of hormone receptor-positive (HR+), human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative (HER2-) advanced or metastatic breast cancer in combination with fulvestrant in women with disease progression following endocrine therapy.1 Pfizer’s supplemental New Drug Application (sNDA) for Ibrance was reviewed and approved under the FDA’s Breakthrough Therapy designation and Priority Review programs based on results from the Phase 3 PALOMA-3 trial in pre-, peri- and post-menopausal women with HR+, HER2- metastatic breast cancer whose disease progressed on or after prior endocrine therapy in the adjuvant or metastatic setting.
Ibrance first was approved in February 2015 and also is indicated for the treatment of HR+, HER2- advanced or metastatic breast cancer in combination with letrozole as initial endocrine-based therapy in postmenopausal women.1 The indication in combination with letrozole is approved under accelerated approval based on progression-free survival (PFS). Continued approval for this indication may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in a confirmatory trial.1 The confirmatory Phase 3 trial, PALOMA-2, is fully enrolled.
Ibrance is the first and only cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 (CDK 4/6) inhibitor approved by the FDA.
Pfizer Receives Expanded FDA Approval For Ibrance (palbociclib) In HR , HER2- Metastatic Breast Cancer

 (
( (Donepezil)
(Donepezil) 

 (Elbasvir)
(Elbasvir)  (Grazoprevir)
(Grazoprevir)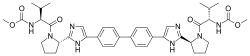
 Tetracaine
Tetracaine